In a globalized and highly uncertain market environment, commodity trading often involves huge amounts, cross-border complexities, and multiple types of counterparties.
Sharp commodity price fluctuations, diverse legal and regulatory frameworks, and fragmented management of credit instruments constantly challenge counterparties’ ability to perform. As a result, credit risk incidents occur frequently.
Therefore, credit risk management has become one of the key measures for trading enterprises to ensure business security and stable development.
Against this backdrop, enterprises face five major pain points in practical credit risk management:
1. Dispersed counterparty information and diverse types
Counterparties are complex—such as physical trading partners, derivatives traders, and brokers. Their information is scattered, with no unified management or transparent display.
2. Lack of transparency in credit status and no unified evaluation standard
It is difficult to gain a comprehensive view of counterparties’ credit status. A standardized evaluation system is missing. Credit approval and risk assessment rely heavily on experience, which is inefficient and prone to overlooking risks.
3. Complex and non-standard credit limit calculation with low efficiency in manual processes
Credit limit calculations are complicated and lack standardization. Manual processing is slow, error-prone, and cannot support complex scenarios such as personalized or shared credit limits.
4. Untimely monitoring of credit risk limits and delayed warnings
Usage of limits, future peaks, and key execution nodes are not monitored in real time. Risks of exceeding limits are hard to detect quickly. Delayed warnings prevent proactive management of potential credit incidents.
5. Fragmented management of credit risk mitigation tools and difficulty in evaluating effectiveness
Mitigation tools such as letters of credit, guarantees, and credit insurance are managed separately.Information is not consolidated, making it hard to measure limit usage or directly evaluate the effectiveness of risk mitigation.
These challenges leave enterprises struggling with fragmented information, inaccurate risk identification, imbalanced limit control, delayed alerts, and unclear mitigation results. They directly weaken credit risk management and undermine business security and stability.
To address this, the Fusion CTRM Credit Management Solution combines standardization with customization. It enables enterprises to achieve systematic, transparent, and efficient credit management.
The following sections will showcase practical results from Company H, Company A, and Company B, demonstrating its effectiveness across different application scenarios.
I. Fusion Credit Management Solution: A Balance of Standardization and Customization
The Fusion Credit Management Solution combines “standardization + customization.”It builds a general management framework while addressing enterprises’ unique needs.
This provides a systematic and practical approach for complex credit management.
It resolves industry pain points and raises the overall level of credit risk management.
(A) Standardization: Building the Foundation of Credit Risk Management and Addressing Common Pain Points
At the standardization level, the solution focuses on the general processes and frameworks of credit risk management.
It offers a solid foundation to resolve common challenges in enterprise credit management.
1. Unified Counterparty Management: Solving Information Fragmentation
The standardized solution supports end-to-end management processes for multiple types of counterparties.
This includes application, approval, management, changes, and periodic reviews.It covers physical trading partners, derivatives traders, brokers, service providers (transportation, shipping agents, warehousing, freight forwarding, inspection, etc.), and financial institutions (banks, insurers, etc.).
The system manages details such as basic information, business type, trading conditions, credit limits, financial statements, rating standards, attachments, and operation records.
It also displays counterparty risk control status, such as active or frozen.
This standardized method effectively resolves the issue of scattered counterparty information.
It enables enterprises to gain a full picture of counterparties, improve query efficiency, and enhance transparency.
2. Comprehensive Credit Risk Evaluation System: Solving Lack of Transparency
To address non-transparent credit status and the absence of a unified evaluation standard, the solution provides a combined qualitative and quantitative rating system.
Internal ratings can rely on financial quantitative indicators or combine qualitative factors such as company size and relative strength.
Different models can be applied to different types and industries of counterparties.
Once indicators are set, weights are assigned and scoring options selected.The scores are aggregated into a total, and a rating is assigned based on score ranges.
External ratings mainly adopt those from international agencies such as S&P, Moody’s, and Fitch.
By integrating internal and external ratings, the system generates a final counterparty rating.
This rating supports admission, management, credit limit setting, and credit term definition.
It gives enterprises a complete and accurate profile, effectively solving credit transparency issues.
3. Standardized Monitoring and Early Warning: Solving Delays in Control and Alerts
To tackle untimely monitoring and delayed warnings, the solution offers both automatic and manual credit limit calculation.It supports calculations for current usage and future peak usage, and shows unreleased and released contracts.
Users can see available limits and over-limit situations.When 80% of the credit limit is reached, the system sends automatic email alerts.
This mechanism ensures real-time monitoring and timely warnings.It allows enterprises to identify potential risks early and take preventive measures.
4. Centralized Management of Credit Risk Mitigation Tools: Solving Fragmentation and Assessment Gaps
For tools such as letters of credit, guarantees, and credit insurance, the solution provides management functions for documents, amounts, contracts, and fees.
Through centralized management, enterprises can easily track limit usage and visually assess mitigation effectiveness.This improves both efficiency and accuracy in credit risk management.
(B) Customization: Tailoring to Enterprise-Specific Needs and Solving Unique Pain Points
The customization level considers differences in credit evaluation standards, credit limit methods, and guarantee practices.It offers tailored services to meet enterprises’ unique requirements.
1. Customized Credit Evaluation Standards: Meeting Diverse Needs
Enterprises have diverse needs and counterparties are complex.Rating models and indicators are therefore highly personalized.
The system allows enterprises to design internal rating standards and customize evaluation indicators.
They can flexibly adjust indicators and weights based on business characteristics.This ensures accurate risk identification, even when standards vary.
2. Personalized Credit Limit Calculations: Supporting Flexible Management
Credit limit calculations vary widely among enterprises.Common methods include sales volume, repayment amount, operating assets, and characteristic analysis.Companies may use one, several, or a custom hybrid approach.
The system supports personalized calculations, with automated processes to boost efficiency and accuracy.It also allows manual management for flexibility.
For complex shared-limit cases, the system manages allocations to ensure accurate credit and available balance calculations.
3. Differentiated Guarantee Management: Matching Business Practices
Credit mitigation and guarantee methods vary, such as letters of credit, guarantees, credit insurance, and wire transfers.Usage differs by enterprise.
The system supports customized management based on common credit terms and guarantees.For example, enterprises that distinguish between long-term and short-term guarantees can manage both effectively within the system.
(C) Data and Business Integration: Enabling Refined Credit Risk Control
Fusion not only balances standardization and customization but also ensures data and business integration across modules.This enables precise credit risk control.
For instance, credit ratings influence transaction terms.High-rated counterparties can enjoy looser terms, while lower-rated ones require stricter ones.If credit terms mismatch with ratings, the system triggers automatic downgrades, prompting enterprises to take risk control measures.
Similarly, dynamic credit limit monitoring involves key dates such as guarantee maturity, bill of lading, and payment dates.Fusion connects credit data with trading, execution, and settlement processes.This grounds credit management in operational details and improves the accuracy of risk warnings.
Through a combination of standardization and customization, along with strong integration of business processes and data, Fusion effectively resolves complex credit management challenges in trading.It meets the need for both personalized and refined management.It improves efficiency and reduces the occurrence of risk incidents.
To make its impact more concrete, the following section will present case studies from Company H, Company A, and Company B, showing how different enterprises implemented the solution and what benefits they achieved.
II. Case Studies of Company H, Company A, and Company B: Differentiated Implementation and Outcomes
In practice, enterprises vary in business structures, risk appetites, and management priorities.
As a result, their applications of credit management solutions differ.Company H, Company A, and Company B are three typical cases.With Fusion’s support, each addressed its own pain points through differentiated implementation, achieving significant and unique results.
Pain Point 1: Scattered Counterparty Information and Diverse Types
Case Implementation:
All three companies used Fusion to achieve unified counterparty file management.Company H, with a wide variety of counterparties, emphasized detailed categorization.Company A and Company B, although with fewer counterparties and business types, also achieved clear and simple management through the system.
Outcome:
All three effectively solved information fragmentation.Query efficiency improved by more than 70% on average, and management transparency rose significantly.
Pain Point 2: Non-Transparent Credit Status and Lack of Standardized Evaluation
Case Implementation:
Company H and Company A adopted Fusion’s combined internal and external credit evaluation system.Company H applied differentiated ratings for different counterparties, integrating external standards.Company A focused more on financial indicators while referencing external rating agencies.Company B did not fully adopt this function.
Outcome:
Transparency of credit evaluations improved significantly at Company H and Company A.Credit approval time was cut by about 50% on average.Credit risk identification improved by about 40%.Enterprises could make more scientific and accurate credit admission decisions, reducing credit risk.
Pain Point 3: Complex, Non-Standard Credit Limit Calculations and Inefficient Manual Processes
Case Implementation:
Company H and Company A used Fusion to automate limit calculations while allowing manual maintenance.Both supported shared-limit scenarios.Company H developed specific calculation models based on guarantees and mitigation tools.Company A combined financial indicators with rating results to set automatic calculation models.Company B did not implement this function.
Outcome:
Accuracy of limit calculations improved by about 60% on average for Company H and Company A.Efficiency and flexibility of credit limit management also improved significantly.
Pain Point 4: Untimely Monitoring and Delayed Warnings of Credit Risk Limits
Case Implementation:
Company H enabled Fusion’s monitoring and early warning function.The system automatically tracked usage, future peaks, released and unreleased amounts.It sent email alerts when limits neared thresholds, and dynamically tracked contract execution for proactive monitoring.Company A and Company B did not enable this function.
Outcome:
Company H improved early detection of over-limit cases by about 80%.Actual default risk incidents dropped by about 30%.
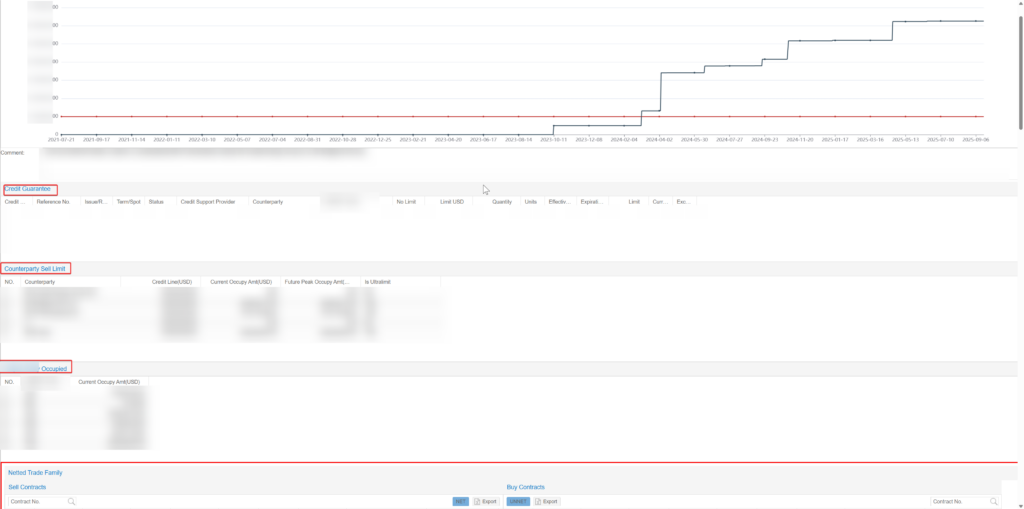
Pain Point 5: Scattered Management of Credit Risk Mitigation Tools and Difficulty in Evaluation
Case Implementation:
Company H centralized management of guarantees, letters of credit, and credit insurance in Fusion, linking them with limit usage statistics.Company A and Company B implemented management for guarantees and letters of credit separately, without integrating limit statistics.
Outcome:
Company H increased guarantee coverage to 85%, and limit transparency improved by 70%.Company A and Company B unified management of mitigation tool information.Their query efficiency and transparency improved by about 40% and 35% respectively.Use of risk mitigation tools became more intuitive and controllable.
Through these cases, it is clear that Fusion’s credit management solution adapts well to different enterprise scenarios and delivers significant results.
Enterprises that enabled relevant functions saw credit management efficiency rise by more than 50% on average.
The occurrence of risk events declined notably.This fully demonstrates Fusion’s value and practical feasibility in commodity credit risk management.
Conclusion: Improving Credit Management Efficiency and Risk Control
From industry pain points to solution design and case validation, the picture is clear.
Fusion enables full-process control in credit risk management:from centralized information to transparent evaluation,from precise limit calculation to proactive risk warnings,and from mitigation tool management to integrated oversight.
Its blend of standardization and customization not only resolves common management challenges but also ensures flexibility in complex scenarios.
These results improve efficiency and accuracy, while reducing risk events.
Fusion’s practice shows that digital and systematic credit management is becoming a core driver of sustainable growth for enterprises.